Indonesia offers a favorable environment for investment, with different regions offering business-friendly policies and investment incentives. However, which regions offer optimal conditions for different industries?
With 17000 islands varying in quality, reliability, and availability of logistics, infrastructure, and utility services, we discuss the potential hot spots for foreign investors when choosing where to invest in Indonesia.
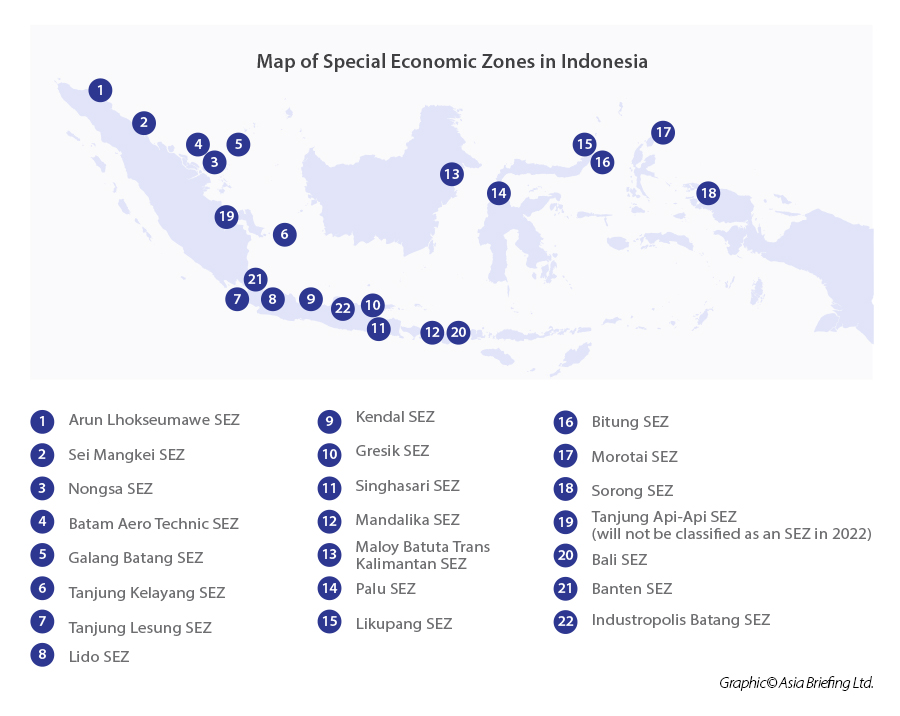
Overview of Indonesia’s key economic regions
For foreign investors, entering Indonesia’s special economic zones (SEZ) and taking full advantage of what they offer requires a long-term outlook.
Companies must first ensure their industry is suited to the infrastructure and benefits afforded in the SEZs and understand the long-term domestic and regional policies that could impact their industry.
There are 22 SEZs in Indonesia. 12 are in operation focusing on manufacturing, and the remainder are in the construction phase. Eight are designated for tourism, three digital SEZ, 1 maintenance, repair, overhaul (MRO) SEZ, and the rest for manufacturing and processing. The government is currently in the process of establishing an additional 8 Special Economic Zones (SEZs), further highlighting its commitment to economic expansion and industrial development.
SEZs are expected to become engines of economic growth by attracting major investment, accelerating industrialization, creating jobs, enhancing Indonesia's global competitiveness, and driving regional development.
Within an SEZ, the following business activities can be undertaken:
- Production and processing;
- Logistics and distribution;
- Research, digital economy, and technology development;
- Tourism;
- Energy development;
- Education;
- Healthcare;
- Sports;
- Financial services;
- Creative industries;
- SEZ development and management; and
- Procurement of SEZ infrastructure.
Investors operating in Indonesia’s SEZs will find they are supported by well-integrated infrastructure from highways, drainage systems, high-speed internet and communication systems, ports, and airports.
Moreover, the Indonesian government has prepared an array of fiscal and non-fiscal incentives, such as easier immigration process, corporate income tax reductions, exemptions on import duties and excise duties, among many others.
For foreign investors, entering Indonesia’s special economic zones and taking full advantage of what they offer requires a long-term outlook. Companies must first ensure their industry is suited to the infrastructure and benefits afforded in the SEZs, as well as understand the long-term domestic and regional policies that could impact their industry.