With its consistent economic growth, strategic location, and comprehensive support for businesses, Malaysia presents decision makers with a robust platform for sustainable growth in the Asia-Pacific market.
Strategic economic position
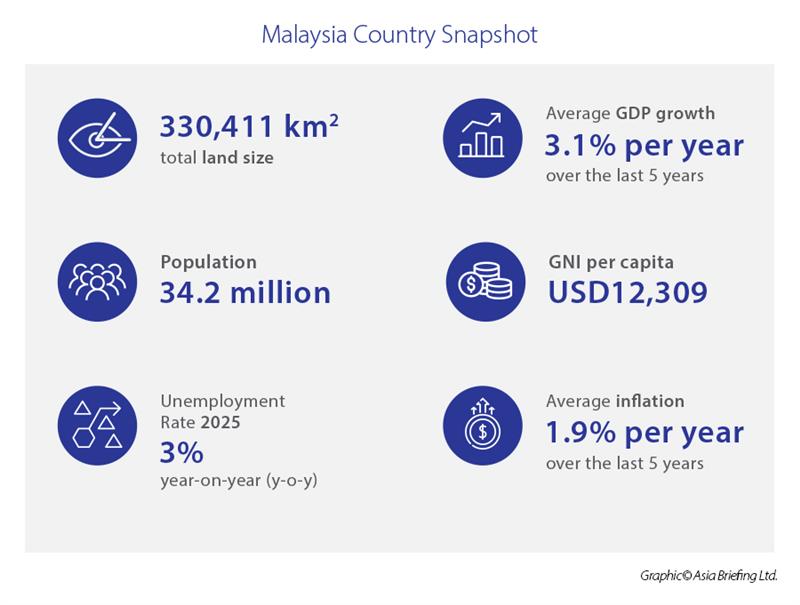
Malaysia's economy has demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth potential, maintaining consistent expansion despite global uncertainties. The country's GDP grew by 4.4 percent in the second quarter of 2025, matching the pace from Q1 and reflecting robust fundamentals across key sectors.
Investment momentum continues to strengthen, with Malaysia securing RM 190.3 billion (US$ 45.1 billion) in approved investments during the first half of 2025, representing an impressive 18.7 percent year-on-year increase. Foreign investors contributed RM 113.4 billion (US$ 26.9 billion) of this total, demonstrating sustained international confidence in Malaysia's economic trajectory. This investment performance builds upon the record-breaking RM 378.5 billion (US$ 89.8 billion) in approved investments achieved in 2024, marking a 14.9 percent increase from the previous year.
The country's implementation rate exceeds 85 percent for manufacturing projects approved since 2021, indicating not only investor confidence but also effective government facilitation and inter-agency collaboration.
Competitive tax framework
Malaysia maintains one of Asia's most competitive corporate tax regimes, offering significant advantages for businesses across different scales of operation. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) with paid-up capital of RM 2.5 million (US$ 593,450) or less and annual income not exceeding RM 50 million (US$ 11.8 million) benefit from a 17 percent corporate tax rate on their first RM 600,000 (US$ 142,000) of income, followed by 24 percent on subsequent earnings.
The Johor-Singapore Special Economic Zone represents a particularly attractive proposition, offering a special corporate tax rate of 5 percent for 15 years for qualifying manufacturing and services activities, including artificial intelligence, quantum computing supply chains, medical devices, and aerospace manufacturing. This incentive package, effective retroactively from January 1, 2025, also provides eligible knowledge workers with a 15 percent income tax rate for 10 years.
Comprehensive investment incentives
Pioneer Status (PS) and Investment Tax Allowance (ITA) form the cornerstone of Malaysia's investment promotion strategy. PS provides exemption from corporate income tax on 70 percent of statutory income for five years, with enhanced benefits for strategic projects including 100 percent exemption for projects of national importance. ITA offers 60 percent deduction on qualifying capital expenditure for five years, applicable against 70 percent of statutory income.
The New Investment Incentive Framework, introduced in 2025, targets high-value activities across 21 economic sectors with special tax incentives contingent upon achieving economic spillovers. Malaysia expects to mobilize over RM 2 billion (US$ 474.4 million) in catalytic capital to support early-stage RandD, product development, and ecosystem scaling under the National Semiconductor Strategy.
World-class infrastructure
Malaysia's strategic location in the heart of ASEAN provides unparalleled access to a consumer base of 667.3 million people across the regional bloc. The country serves as a gateway to major shipping routes in the South China Sea, with its ports handling significant portions of regional and international trade.
Port infrastructure represents a critical competitive advantage, with Port Klang ranking among the busiest ports in the region, handling millions of containers annually. The port ecosystem includes Penang Port, Port of Tanjung Pelepas, and several other strategic facilities that provide comprehensive coverage for different cargo types and regional connectivity.
Malaysia's transportation infrastructure encompasses extensive road networks, modernized rail systems, and world-class airports that facilitate efficient cargo movement. The North-South Expressway provides seamless connectivity between northern and southern regions, while ongoing rail network modernization improves bulk commodity and heavy machinery transport capabilities.
Kuala Lumpur International Airport (KLIA) has emerged as a key regional air cargo hub, with dedicated cargo terminals and expanding airfreight services enhancing Malaysia's attractiveness for time-sensitive, high-value shipments. The Malaysia freight logistics market, valued at US$ 27.5 billion in 2022, is projected to reach US$ 43.39 billion by 2032, reflecting a robust 5.20 percent CAGR.
Highly skilled workforce
Malaysia boasts 20 public universities and over 80 private universities, complemented by more than 1,400 technical and vocational education and training (TVET) colleges, creating one of the region's most educated workforces. The country's literacy rate of 97.51 percent reflects the government's sustained commitment to human capital development.
Multilingual capabilities represent a distinctive competitive advantage, with most Malaysians proficient in at least two to three languages, including high levels of English proficiency alongside Bahasa Malaysia, Mandarin, and Tamil.
English proficiency specifically serves as a gateway to employment and higher salaries, with employers consistently ranking English communication among top hiring criteria. Studies demonstrate that English competence correlates with wage premiums and broader labor market mobility, particularly in sectors linked to global value chains.
The Malaysian Education Blueprint 2013-2025 prioritizes STEM education enhancement, exposing students to programming, robotics, artificial intelligence, and computer science. The government has allocated RM 10 billion (US$ 2.3 billion) annually for skills-related education and training, with approximately 30 percent funded through statutory contributions.
Workforce development initiatives target 60,000 semiconductor engineers to support the expanding high-tech sector. The National Semiconductor Strategy emphasizes talent development across the full semiconductor value chain, positioning Malaysia to address global engineer shortages while building domestic capabilities.
Extensive free trade agreement network
Malaysia maintains 16 Free Trade Agreements (7 bilateral, 9 regional) covering approximately 67 percent of the country's total trade. These agreements provide reduced tariffs, harmonized standards, and streamlined cross-border procedures that significantly enhance market access for businesses operating from Malaysia.
Key regional agreements include the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) linking Malaysia to 660 million consumers, the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) covering the world's largest trading bloc, and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) providing duty-free channels to major Asia-Pacific economies.
Bilateral FTAs with Australia, Japan, New Zealand, and other major economies extend market reach to over three billion consumers. The recent UK accession to CPTPP, entering force between the UK and Malaysia on December 15, 2024, creates the first-ever free trade agreement between the two countries.
RCEP's unified rules of origin facilitate seamless duty-free trade across 15 member economies, while CPTPP is projected to boost Malaysia's total trade to US$ 655 billion by 2030. These agreements eliminate duties on up to 98.7 percent of tariff lines under AFTA and target 92 percent coverage under RCEP over the next two decades.
Digital transformation ecosystem
Malaysia's digital economy contributed 23.2 percent of GDP in 2023 and is projected to reach 25.5 percent by end-2025. Approved digital investments reached RM 163.6 billion (US$ 38.8 million) in 2024, representing a 250 percent year-on-year increase that demonstrates accelerating digitization across sectors.
The National Semiconductor Strategy positions Malaysia as a comprehensive semiconductor hub spanning design, manufacturing, testing, and packaging. Recent investments from Intel, Infineon, Google, and Nvidia totaling billions of dollars underscore global confidence in Malaysia's high-tech capabilities.
Malaysia's fintech market was valued at US$ 46.6 billion in 2024, with a projected 13.2 percent CAGR through 2030. The sector increasingly attracts foreign investment as Malaysia consolidates its position as a regional financial hub with sophisticated Islamic banking capabilities.
Five licensed digital banks now operate in Malaysia, offering innovative solutions and competitive services that enhance the financial ecosystem for businesses.
Investment protection
Malaysia has established Investment Guarantee Agreements (IGAs) with over 60 countries, including major economies such as the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Japan, China, and Australia. These agreements provide legal protection and dispute resolution mechanisms for foreign investments.
Political stability and consistent pro-business policies spanning multiple government administrations provide confidence for long-term investment planning. The country's rule of law framework and independent judiciary ensure investor rights protection and contract enforcement.
Economic resilience
Malaysia's diversified economic base spanning manufacturing, services, agriculture, and natural resources provides resilience against sector-specific downturns. Strong domestic fundamentals, including healthy labor market conditions and modest inflation projected at 1.5 percent-2.5 percent in 2025, support sustained economic growth.
The RM's emergence as Asia's best-performing currency during recent periods reflects underlying economic strength and investor confidence. Fiscal consolidation efforts supported by reduced subsidies and expanded taxation demonstrate responsible economic management.
Summary: Top 10 Reasons to Invest in Malaysia
|
Number |
Reason |
Highlight |
|
1 |
Strategic economic position |
Malaysia’s economy grew 4.4% in Q2 2025, with RM 190.3 billion (US$ 45.1 billion) in approved investments in just the first half of the year — a clear sign of resilience and global investor confidence. |
|
2 |
Competitive tax framework and incentives |
With a 17%–24% corporate tax range and special packages like the Johor-Singapore SEZ (5% tax for 15 years), Malaysia offers one of Asia’s most competitive business tax regimes. |
|
3 |
Comprehensive investment incentive programs |
Incentives like Pioneer Status (up to 100% tax exemption) and Investment Tax Allowance (60% capital deduction) encourage innovation, advanced manufacturing, and RandD. |
|
4 |
World-class infrastructure and connectivity |
Strategically located in ASEAN, Malaysia hosts major trade gateways like Port Klang (one of the busiest in the region) and KLIA, a leading regional air cargo hub, supported by modern highways and rail. |
|
5 |
Highly skilled and multilingual workforce |
With a 97.5% literacy rate, over 100 universities, and a government plan to train 60,000 semiconductor engineers, Malaysia offers a well-educated and multilingual talent pool. |
|
6 |
Extensive Free Trade Agreement (FTA) networks |
Through 16 FTAs covering 67% of total trade, Malaysia connects businesses to over 3 billion consumers, including access via ASEAN, RCEP, and CPTPP. |
|
7 |
Digital transformation and innovation ecosystem |
The digital economy already contributes 23.2% of GDP, expected to reach 25.5% by 2025. Global tech leaders like Intel, Nvidia, and Google are investing billions in Malaysia. |
|
8 |
Risk management and investment protection |
With 60+ Investment Guarantee Agreements and a strong legal framework, Malaysia provides investors with stability, protection, and reliable dispute resolution mechanisms. |
|
9 |
Economic resilience and diversification |
A diversified economy — from manufacturing to services and resources — keeps growth stable. Inflation remains low (1.5%–2.5% in 2025) and the RM is one of Asia’s best-performing currencies. |
|
10 |
Proven Track Record of Investment Implementation |
Over 85% of approved manufacturing projects since 2021 have been implemented, showcasing effective government support and real execution power. |











