Insights into Malaysia’s Standing in the 2024 Emerging Asia Manufacturing Index
The Emerging Asia Manufacturing Index 2024 report (“EAMI 2024”) published by Dezan Shira & Associates provides insights into the factors that influence the manufacturing sector in selected countries in Asia namely Indonesia, China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Thailand, India, and Bangladesh.
The report highlights Malaysia’s potential as a stable manufacturing destination for foreign investors, supported by a supportive labor market, a well-capitalized financial sector, and developed infrastructure.
The assessment in the report relies heavily on evaluating 48 specific parameters structured across eight key criteria: economy, political stability, business climate, global trade, taxation, infrastructure, labor force, and innovation.
Analyzing key parameters
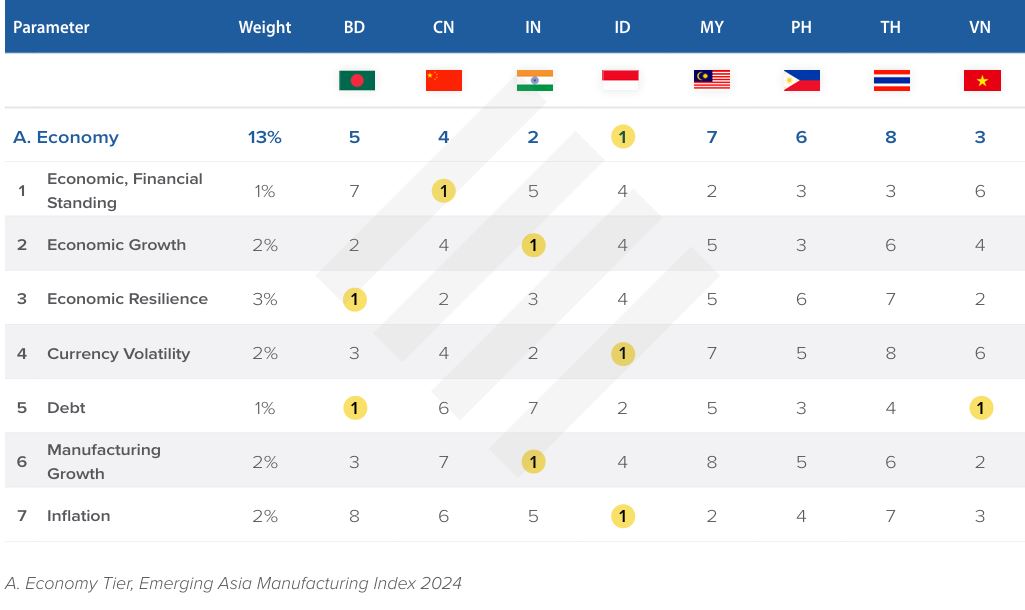
Economic tier
Malaysia’s economic tier is ranked seventh in the report. The country’s economic growth and resilience are also ranked fourth and are ranked second for national debt.
Malaysia is one of Asia’s major electronics production hubs with the country responsible for 13 percent of global chip production, testing, and packaging, in addition to seven percent of global semiconductor production.
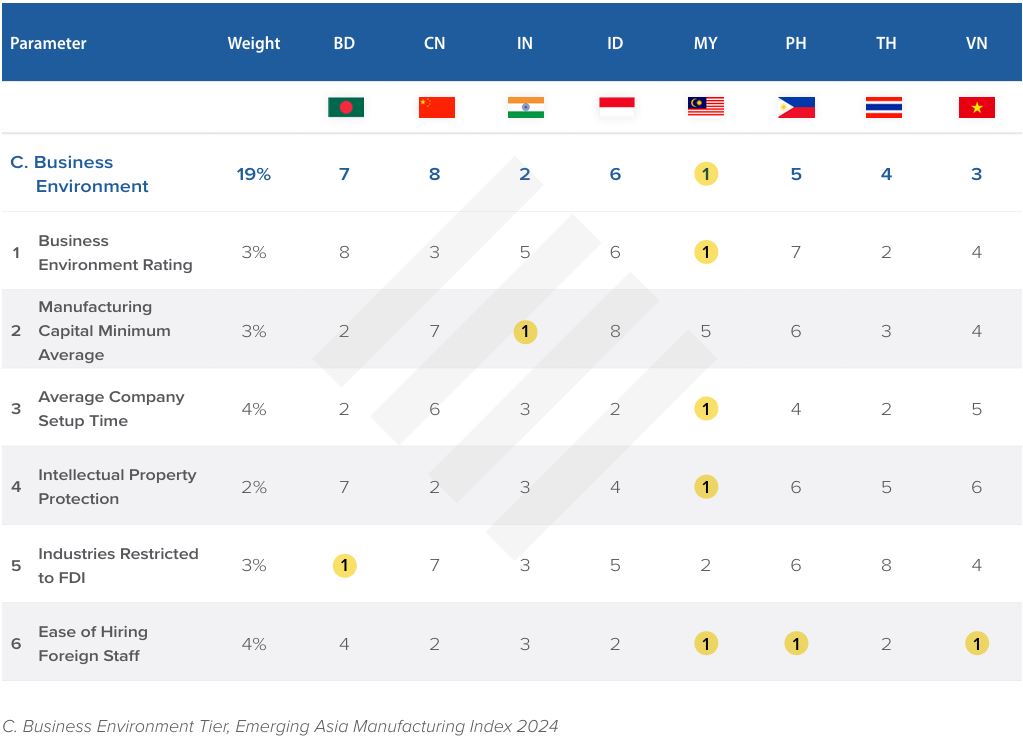
Business environment
Malaysia’s business environment was ranked first. Further, the country was also ranked first for average company setup time, intellectual property protection, and the ease of hiring foreign staff.
Malaysia offers a diverse array of business models that attract multinational corporations (MNCs), including Global and Regional Headquarters, Centres of Excellence (COEs), and Procurement and Distribution Hubs. These models provide MNCs with numerous advantages, making Malaysia an ideal strategic hub in the Asia-Pacific region for efficiently managing service operations and regional or global supply chains.
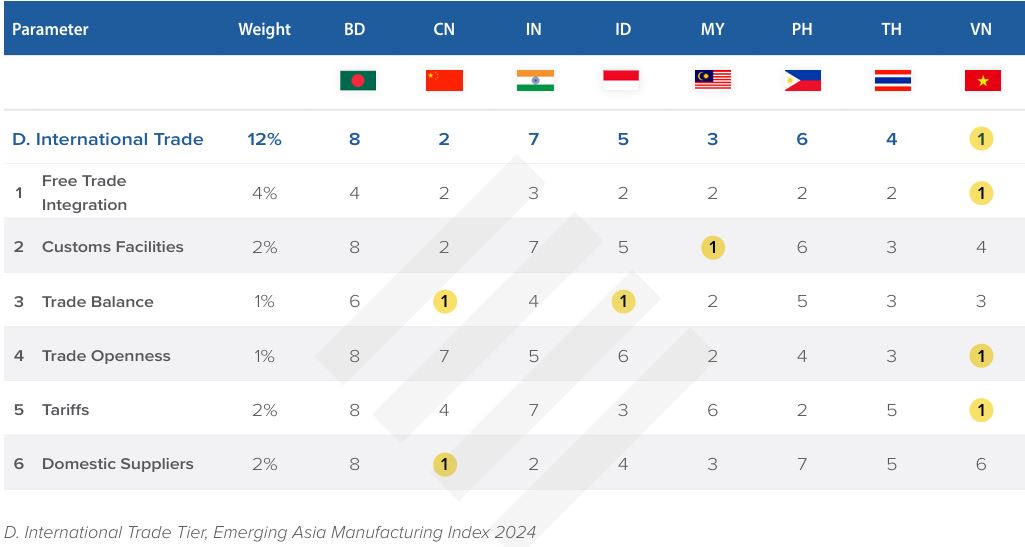
International trade
In the report, Malaysia’s overall international trade rank was third. The country’s customs facilities were ranked first, trade balance was ranked second, and trade openness was also ranked second.
Malaysia boasts an open economy driven by trade in goods and services. Over the years, the country has established an extensive network of regional and bilateral trade agreements, enabling Malaysia-based exporters and investors to benefit from tariff concessions, expanded market access, and strengthened economic integration with partner nations and regions. Consequently, Malaysia’s robust international trade activities have been instrumental in driving sustained economic growth and overall development, cementing the nation’s status as a prominent player in the global marketplace.
Recognizing international trade and investment as key drivers of economic growth, Malaysia has ratified seven bilateral Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with Australia, Chile, India, Japan, New Zealand, Pakistan, and Turkiye.
Additionally, Malaysia, alongside its ASEAN partners, participates in several trade agreements, including the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), ASEAN-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (AJCEP), ASEAN-Korea Free Trade Agreement (AKFTA), ASEAN-China Free Trade Agreement (ACFTA), ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (AANZFTA), ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement (AIFTA), and ASEAN-Hong Kong Free Trade Agreement (AHKFTA).
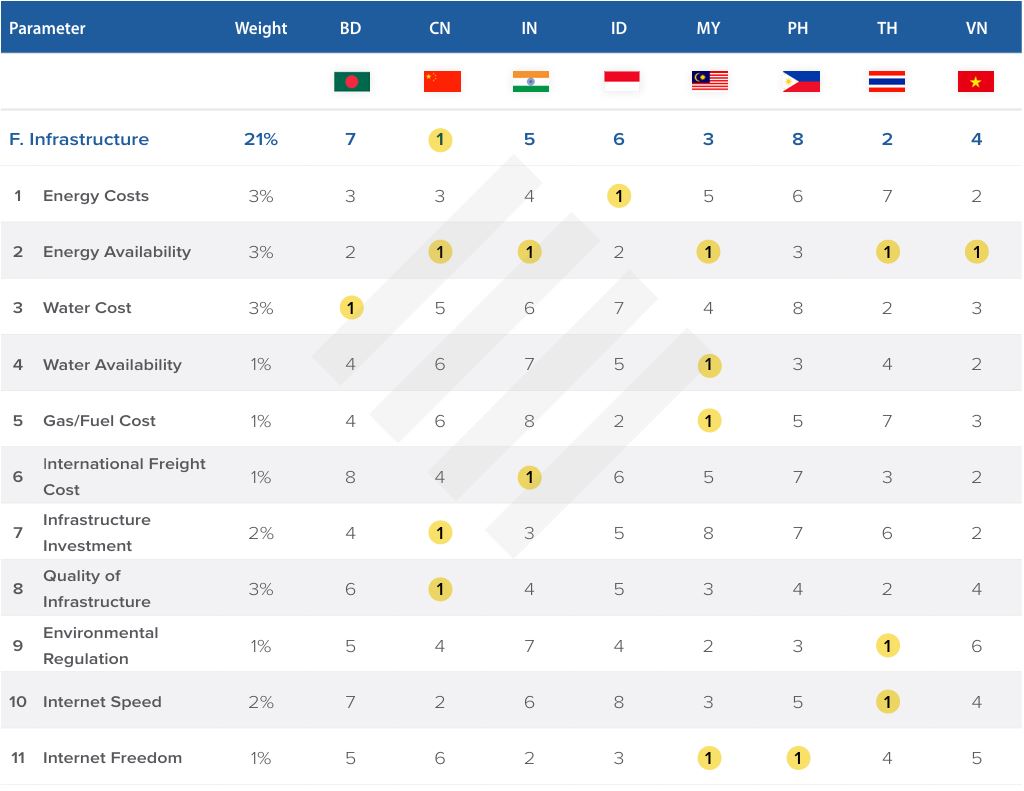
Infrastructure tier
The EAMI index placed Malaysia’s infrastructure ranking as third from eighth. The country also ranked first for energy availability, first for water availability, and first for fuel costs.
Malaysia is well served with over 94,000km of primary and secondary roads and over 500km of highways. The country also has over 1,800km of railway and over 30 airports. The largest is the Kuala Lumpur International Airport which can handle some 25 million passengers and 1.2 million tons of cargo annually.
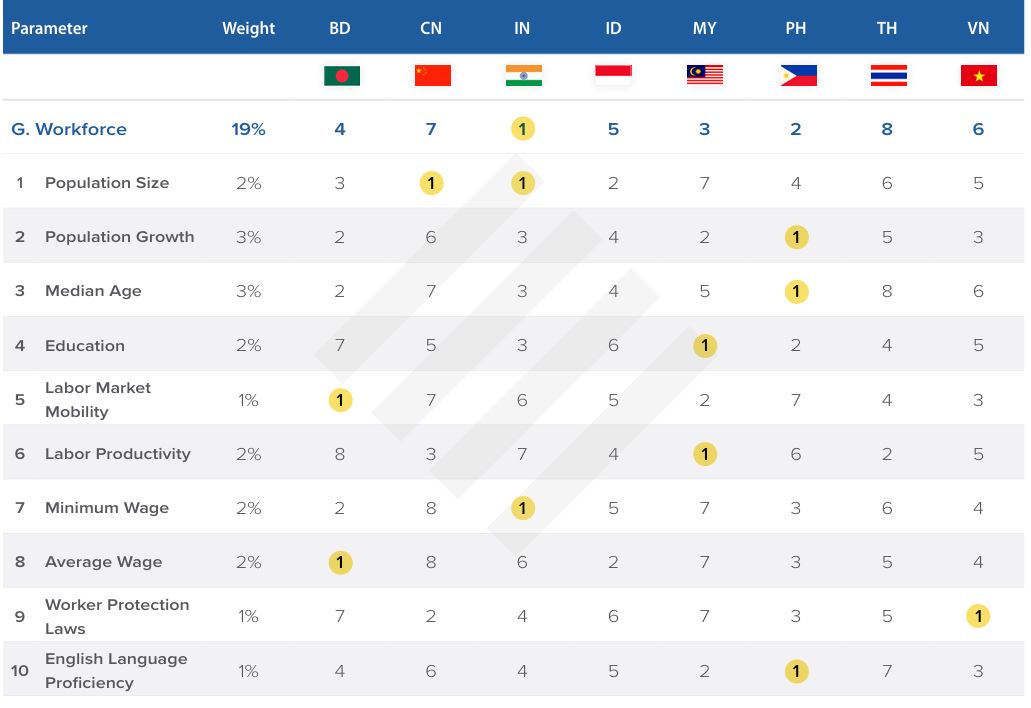
Workforce tier
The EAMI report ranks Malaysia’s workforce tier as third. The country was ranked seventh for its population size and seventh for average wages. Malaysia was ranked first for education labor productivity.
Malaysia, particularly Greater KL produced some of the region’s most educated and highly skilled workforce, playing a key role in driving innovation, nurturing economic growth, and attracting global investments. Its multilingual talents give MNCs a competitive advantage in navigating a diverse market.
This is evident with the 2022 Global Talent Competitiveness Index, Malaysia was ranked 45th out of 133 countries. This ranking demonstrates the dynamic talent landscape in Greater KL, showcasing the ability to attract and nurture a highly skilled, multilingual workforce, thus positioning the city as a hub for global business activities.
The Malaysian Education Blueprint of 2015-2025 further promotes the strategic partnership between universities and industries by allowing businesses to collaborate on curriculum design, particularly in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). It highlights the government’s commitment to upskilling the workforce, ensuring they stay ahead of the curve in this space.
The government is also investing substantially in digital talent through initiatives such as The National Digital Skills Strategy. Launched in 2019, it aims to equip Malaysians with digital competencies. With the rising global demand for specialized digital skills such as cybersecurity, generative AI, and the Internet of Things (IoTs) to meet this demand, Malaysia aims to produce an estimated 20,000 cybersecurity experts by 2025.
About Us
ASEAN Briefing is produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The firm assists foreign investors throughout Asia and maintains offices throughout ASEAN, including in Singapore, Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, and Da Nang in Vietnam, in addition to Jakarta, in Indonesia. We also have partner firms in Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand as well as our practices in China and India. Please contact us at asean@dezshira.com or visit our website at www.dezshira.com.








