FTSE & ASEAN Join Together Over Joint Indices
May 10 – The FTSE Group and five ASEAN stock exchanges (the Bursa Malaysia Exchange, the Indonesian Stock Exchange, the Philippines Stock Exchange, the Singapore Stock Exchange and the Stock Exchange of Thailand) have joined forces to launch a unique and innovative set of indices known as the FTSE/ASEAN Index series.
The FTSE/ASEAN venture provides two indices:
- the FTSE/ASEAN Index – a benchmark index that provides an indication of the financial performance of the large and mid-sized companies from the five countries comprising the ASEAN region; and
- the FTSE/ASEAN 40 – a tradable index consisting of the top 40 constituents from the FTSE/ASEAN index (ranked by market capitalization).
The FTSE/ASEAN 40 Index is calculated Monday through Friday from 09:00 local Singaporean time until each of the constituent markets have closed. The closing index value is calculated at 18:00 local Singapore time.
The FTSE/ASEAN Index is calculated at the end of the day Monday through Friday at 18:00 local Singaporean time.
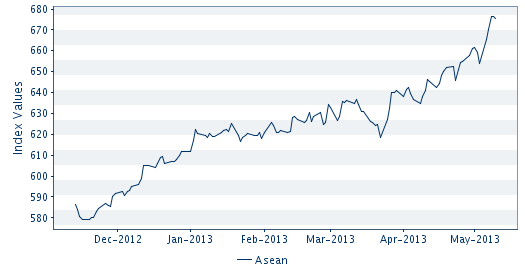
The trading of the FTSE/ASEAN Index has been highly positive over the past six months, as demonstrated in the graph from FTSE below:
Please find a short history of each of the component Stock Exchanges below.
The Malaysian Stock Exchange was previously known as the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange Berhad (KLSE), which originated in 1930 when the Singapore Stockbrokers’ Association established a formal organization to deal with securities.
Afterwards, in 1964, the Stock Exchange of Malaysia was established. After Singapore seceded from Malaysia in 1965, the Stock Exchange of Malaysia became known as the Stock Exchange of Malaysia and Singapore, which was then divided into the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange Berhad and the Stock Exchange of Singapore.
On April 14, 2004, the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange Berhad was renamed Bursa Malaysia Berhad in order to enhance its competitiveness, and today, Bursa Malaysia is an exchange holding company fully approved under Section 15 of the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007. It is licensed to operate as a fully integrated exchange, and it offers a complete range of exchange-related services including trading, clearing, settlement and depository services.
Indonesia has always had an exchange market, even prior to its independence. The first stock exchange in Indonesia was established in 1912 during the Dutch colonial era. The capital market grew rapidly until it was closed during World War II. It was then reopened in 1977, and grew into the Jakarta Stock Exchange (JSX). JSX then became known as the Indonesia Stock Exchange after it merged with the Surabaya Stock Exchange (SSX) in 2007.
As of the end of 2012, the Indonesia Stock Exchange has 462 listed companies with a combined market capitalization of US$426.78 billion.
The Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE) was formed on December 23, 1992 as a composite of the Philippines’ two former stock exchanges, the Manila Stock Exchange (MSE) and the Makati Stock Exchange (MkSE). It is one of the oldest stock exchanges in Southeast Asia, as MSE was established in 1927.
In 2001, the PSE was transformed into a shareholder-based, revenue-earning corporation complete with a president and board of directors.
The main index is the PSE Composite Index (PSEi), which is composed of thirty listed companies.
The Singapore Stock Exchange (SGX) was formed on December 1, 1999 as a holding company to hold the share capital of various Singapore-based companies, namely the Stock Exchange of Singapore (SES), the Singapore International Monetary Exchange (Simex) and Securities Clearing and Computer Services Pte Ltd (SCCS). However, the share capital was cancelled, and new shares issued in these companies were fully paid up by SGX – a move that allowed all previously owned assets to be transferred to SGX.
Companies listed on SGX belong to either one of two groups:
- companies listed on the SGX Mainboard; or
- companies listed on SGX SESDAQ.
To be listed on the mainboard a company needs to fulfill certain requirements as set forth by SGX. A listing on SESDAQ does not need to fulfill any conditions.
As of January 2010, SGX had 774 listed companies with a combined market capitalization of S$650 billion (US$530 billion), with revenues mainly being derived from the securities market (75 percent) and derivatives market (25 percent).
![]() The Stock Exchange of Thailand
The Stock Exchange of Thailand
The Thai Stock Exchange originated back in the early 1960s when Thailand implemented its first two five-year National Economic and Social Development Plans, during which a securities market was proposed to be established to aid with the country’s economic development.
In May 1974, the government issued legislation to establish The Securities Exchange of Thailand (SET) to be located in Bangkok, which started trading on April 30, 1975. Its name was formally changed to The Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET) in 1991.
As of December 31, 2011, the SET – which consists of the SET Index, SET50 Index and SET100 Index – had 545 listed companies with a combined market capitalization of BT฿8,490 billion (US$290 million).
- Previous Article Indonesia Ponders TPP Membership
- Next Article First Round of RCEP Negotiations Conclude

 Bursa Malaysia
Bursa Malaysia The Indonesia Stock Exchange
The Indonesia Stock Exchange The Philippine Stock Exchange
The Philippine Stock Exchange The Singapore Stock Exchange
The Singapore Stock Exchange







